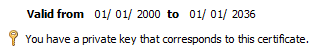Difference between revisions of "Using Your Own SSL Certificate"
| [checked revision] | [unchecked revision] |
Ltalaschus (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Background == | == Background == | ||
During the installation of MailStore Server, an SSL certificate is generated which all MailStore Server components use when an encrypted connection is to be established. Since the certificate is issued to the server name ''MailStoreServer'' and does not come from a reliable certification authority (CA), it is not trusted by the client side. | During the installation of MailStore Server, an SSL certificate is generated which all MailStore Server components use when an encrypted connection is to be established. Since the certificate is issued to the server name ''MailStoreServer'' and does not come from a reliable certification authority (CA), it is not trusted by the client side. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:MSnotrust.png|300px|center]] | [[File:MSnotrust.png|300px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | To eliminate warning and increase security as well as enhance usability, MailStore needs to be reconfigured to use your own certificate. | ||
| − | + | If the ''Personal'' certificate store of the ''Computer account'' does already contain the desired certificate, follow the instructions in the <LINK HERE> section. | |
| − | + | == Creating a New Certificate == | |
| + | Unless a certificate for the host name that is to be used for accessing MailStore Server already exists, follow the below instructions to create a new certificate and import it into Windows' certificate store. | ||
| − | == Creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) == | + | === Creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) === |
| − | + | The following describes how to generate a certificate signing request by using the ''certreq'' tool. ''certreq'' is available by default in most Windows versions. | |
* Log on to the MailStore Server computer. | * Log on to the MailStore Server computer. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 44: | ||
[EnhancedKeyUsageExtension] | [EnhancedKeyUsageExtension] | ||
OID = 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 ; this is for Server Authentication | OID = 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 ; this is for Server Authentication | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Extensions] | ||
| + | 2.5.29.17 = "{text}" | ||
| + | _continue_ = "DNS=*.example.com&" | ||
| + | _continue_ = "DNS=mailstoreserver.example.com&" | ||
| + | _continue_ = "DNS=mailstoreserver&" | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
* Adjust the ''Subject'' and ''FriendlyName'' values according to your needs. | * Adjust the ''Subject'' and ''FriendlyName'' values according to your needs. | ||
| + | * Adjust the ''Subject Alternative Names (SAN)'' in the ''[Extensions]'' section as well. Please note that the ''Common Name (CN)'' in the ''Subject'' is irrelevant for the verification by clients and that all host names must be included as SANs. Additional host names may be added with appending additional ''_continue_'' lines. | ||
* Save the file. | * Save the file. | ||
* Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to the directory where the ''request.inf'' is stored. | * Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to the directory where the ''request.inf'' is stored. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 58: | ||
certreq -new request.inf request.csr | certreq -new request.inf request.csr | ||
| − | = | + | === Validating the Certificate Signing Request === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == Validating the Certificate Signing Request == | ||
To verify that the CSR is correct, execute the following command to display it in a human readable format: | To verify that the CSR is correct, execute the following command to display it in a human readable format: | ||
certutil -dump request.csr | certutil -dump request.csr | ||
| − | == Submitting the Certificate Signing Request == | + | === Submitting the Certificate Signing Request === |
| − | Submit the CSR to your preferred CA. | + | Submit the CSR to your preferred CA. Typically you upload the CSR file to a website of the CA. The CA might ask for the server platform during the submission process. Selecting ''IIS 7'' or ''None of the listed'' should be sufficient. After successful approval of the CSR, you will get the signed certificate in return. |
<p class="msnote">'''Please note:''' Nowadays the certificate mostly is signed by intermediate CAs. It is required that the certificate of the intermediate CA is imported into the certificate store. Detailed information about the installation process of intermediate CA certificates is typically included in the electronic delivery of your certificate.</p> | <p class="msnote">'''Please note:''' Nowadays the certificate mostly is signed by intermediate CAs. It is required that the certificate of the intermediate CA is imported into the certificate store. Detailed information about the installation process of intermediate CA certificates is typically included in the electronic delivery of your certificate.</p> | ||
| − | == ' | + | === Importing the Certificate === |
| − | * Log on to the | + | * Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to the directory where the certificate file is stored. |
| − | * | + | * Execute the following command to import the certificate into the computer's personal certificate store: |
| − | * | + | |
| − | + | certreq -accept certificate.cer | |
| − | * Select '' | + | |
| − | + | === Verifying the Import === | |
| − | * | + | * Log on to the MailStore Server computer as administrator. |
| − | + | * Open the ''Microsoft Management Console (MMC)'' | |
| − | + | * Add the Certificate Snap-In by following these steps: | |
| − | + | ** Click on ''File'' > ''Add/Remove Snap-In'' > ''Certificate'' > ''Add >'' | |
| − | * | + | ** Select ''Computer Account'' and click on ''Next >'' |
| − | * | + | ** Select ''Local Computer'' and click on ''Finish'' |
| + | ** Close any open dialog windows | ||
| + | * Click on ''Certificates (Local Computer)'' > ''Personal'' > ''Certificates'' | ||
| + | * Double-click on the previously imported certificate | ||
| + | * Make sure that the private key for the certificate is available: | ||
[[File:Private_key.png|center]] | [[File:Private_key.png|center]] | ||
| − | + | ==== Repairing the certificate store ==== | |
| + | Sometimes the matching private key cannot be found although the certificate was imported successfully into the correct certificate store. Try to repair the certificate store as follows: | ||
| − | + | * Open an elevated PowerShell and execute the following command: | |
| − | * Open an elevated PowerShell and | ||
Get-ChildItem Cert:\LocalMachine\My | select Subject, Serialnumber, Thumbprint, HasPrivateKey | Get-ChildItem Cert:\LocalMachine\My | select Subject, Serialnumber, Thumbprint, HasPrivateKey | ||
| − | * | + | * Check the subjects, serialnumbers and fingerprints of the installed certificates, to identify the certificate to be used by MailStore. |
| + | * Repair the corresponding certificate store by executing the following command, where ''SerialNumber'' is the serial number of the certificate that should be used. | ||
certutil -repairstore my SerialNumber | certutil -repairstore my SerialNumber | ||
| − | == | + | === Using the Certificate with MailStore Server === |
| − | * Open | + | * Open the MailStore Server Service Configuration. |
| − | * | + | * Select ''IP Addresses and Ports''. |
| + | * In the section you want to change to certificate for, click on the button next to the ''Server Certificate'' field and select ''Select from Certificate Store...'' | ||
| + | * Choose the new certificate from the certificate store. | ||
| + | * Confirm your selection and restart the MailStore Server service. | ||
| − | + | == Importing an Existing Certificate == | |
| − | + | Typically certificates are exchanges between computers by means of Personal Information Exchange (PFX) containers. These can, for example, be created using the export functions of the MMC Snap-In ''Certificates''. | |
| − | + | == Optional: Creating a PFX Container with OpenSSL/LibreSSL == | |
| + | When the original CSR was not created with Windows' own tools or not even created on a Windows computer, it is unlikely that the private key or the vertificate is available in Windows' certificate store of the MailStore Server computer, but on stored on the file system instead. | ||
| − | + | In this case, a Personal Information Exchange (PFX) container need to be created first. This needs to contain the certificate, private key, and all certificates of the certificate chain. After that, the PFX container can by imported into Windows' certificate store. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The following steps need to be executes to convert the certificate files into a PFX container with OpenSSL or LibreSSL: | |
| − | |||
| − | * Copy certificate, private key and the certificates of the certificate chain into the OpenSSL directory. | + | * Copy the certificate, private key and the certificates of the certificate chain into the OpenSSL or LibreSSL directory. |
| − | * Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to | + | * Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to this directory. |
* Create the PFX container by executing the following command, adjust the file names of necessary: | * Create the PFX container by executing the following command, adjust the file names of necessary: | ||
openssl pkcs12 -export -out certificate.pfx -inkey privateKey.key -in certificate.crt -certfile CACert.crt | openssl pkcs12 -export -out certificate.pfx -inkey privateKey.key -in certificate.crt -certfile CACert.crt | ||
| − | * Import the | + | |
| − | + | === Importing a PFX container === | |
| + | * Open the MailStore Server Service Configuration. | ||
| + | * Select ''IP Addresses and Ports''. | ||
| + | * In the section you want to change to certificate for, click on the button next to the ''Server Certificate'' field and select ''Import from file...'' | ||
| + | * Choose the PFX file. | ||
| + | * If the PFX file has been password protected, you are being ask to provide the password now. | ||
| + | * Confirm your selection and restart the MailStore Server service. | ||
== Weblinks == | == Weblinks == | ||
| Line 130: | Line 135: | ||
* [https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732443.aspx Microsoft Technet: Certutil] | * [https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732443.aspx Microsoft Technet: Certutil] | ||
* [https://technet.microsoft.com/de-de/library/ff625722.aspx Microsoft Technet: How to Request a Certificate With a Custom Subject Alternative Name] | * [https://technet.microsoft.com/de-de/library/ff625722.aspx Microsoft Technet: How to Request a Certificate With a Custom Subject Alternative Name] | ||
| − | * [https://www.openssl.org/docs/apps/openssl.html OpenSSL | + | * [https://www.libressl.org/ LibreSSL] |
| + | * [https://www.openssl.org/docs/apps/openssl.html OpenSSL Dokumentation] | ||
| + | |||
[[de:Verwendung_eigener_SSL_Zertifikate]] | [[de:Verwendung_eigener_SSL_Zertifikate]] | ||
[[en:Using Your Own SSL Certificate]] | [[en:Using Your Own SSL Certificate]] | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 17 January 2018
Background
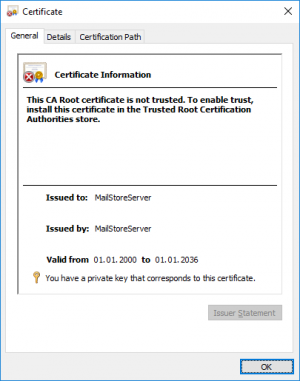
During the installation of MailStore Server, an SSL certificate is generated which all MailStore Server components use when an encrypted connection is to be established. Since the certificate is issued to the server name MailStoreServer and does not come from a reliable certification authority (CA), it is not trusted by the client side.
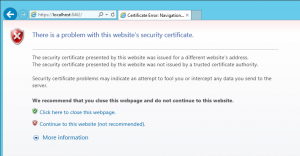
Because of this, the following or a similar warning message is displayed when calling up MailStore Web Access via HTTPS (SSL):
To eliminate warning and increase security as well as enhance usability, MailStore needs to be reconfigured to use your own certificate.
If the Personal certificate store of the Computer account does already contain the desired certificate, follow the instructions in the <LINK HERE> section.
Creating a New Certificate
Unless a certificate for the host name that is to be used for accessing MailStore Server already exists, follow the below instructions to create a new certificate and import it into Windows' certificate store.
Creating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
The following describes how to generate a certificate signing request by using the certreq tool. certreq is available by default in most Windows versions.
- Log on to the MailStore Server computer.
- Prepare a text file request.inf with the following content:
;----------------- request.inf -----------------
[Version]
Signature="$Windows NT$"
[NewRequest]
; replace Subject attributes in the line below with real values
Subject = "CN=mailstoreserver.example.com, OU=Department, O=Organisation, L=Locality, S=State, C=Country"
KeySpec = 1
KeyLength = 2048
Exportable = TRUE
FriendlyName = mailstoreserver.example.com
MachineKeySet = TRUE
SMIME = False
PrivateKeyArchive = FALSE
UserProtected = FALSE
UseExistingKeySet = FALSE
ProviderName = "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider"
ProviderType = 12
RequestType = PKCS10
KeyUsage = 0xa0
[EnhancedKeyUsageExtension]
OID = 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 ; this is for Server Authentication
[Extensions]
2.5.29.17 = "{text}"
_continue_ = "DNS=*.example.com&"
_continue_ = "DNS=mailstoreserver.example.com&"
_continue_ = "DNS=mailstoreserver&"
- Adjust the Subject and FriendlyName values according to your needs.
- Adjust the Subject Alternative Names (SAN) in the [Extensions] section as well. Please note that the Common Name (CN) in the Subject is irrelevant for the verification by clients and that all host names must be included as SANs. Additional host names may be added with appending additional _continue_ lines.
- Save the file.
- Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to the directory where the request.inf is stored.
- Create the CSR by executing the following command:
certreq -new request.inf request.csr
Validating the Certificate Signing Request
To verify that the CSR is correct, execute the following command to display it in a human readable format:
certutil -dump request.csr
Submitting the Certificate Signing Request
Submit the CSR to your preferred CA. Typically you upload the CSR file to a website of the CA. The CA might ask for the server platform during the submission process. Selecting IIS 7 or None of the listed should be sufficient. After successful approval of the CSR, you will get the signed certificate in return.
Please note: Nowadays the certificate mostly is signed by intermediate CAs. It is required that the certificate of the intermediate CA is imported into the certificate store. Detailed information about the installation process of intermediate CA certificates is typically included in the electronic delivery of your certificate.
Importing the Certificate
- Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to the directory where the certificate file is stored.
- Execute the following command to import the certificate into the computer's personal certificate store:
certreq -accept certificate.cer
Verifying the Import
- Log on to the MailStore Server computer as administrator.
- Open the Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
- Add the Certificate Snap-In by following these steps:
- Click on File > Add/Remove Snap-In > Certificate > Add >
- Select Computer Account and click on Next >
- Select Local Computer and click on Finish
- Close any open dialog windows
- Click on Certificates (Local Computer) > Personal > Certificates
- Double-click on the previously imported certificate
- Make sure that the private key for the certificate is available:
Repairing the certificate store
Sometimes the matching private key cannot be found although the certificate was imported successfully into the correct certificate store. Try to repair the certificate store as follows:
- Open an elevated PowerShell and execute the following command:
Get-ChildItem Cert:\LocalMachine\My | select Subject, Serialnumber, Thumbprint, HasPrivateKey
- Check the subjects, serialnumbers and fingerprints of the installed certificates, to identify the certificate to be used by MailStore.
- Repair the corresponding certificate store by executing the following command, where SerialNumber is the serial number of the certificate that should be used.
certutil -repairstore my SerialNumber
Using the Certificate with MailStore Server
- Open the MailStore Server Service Configuration.
- Select IP Addresses and Ports.
- In the section you want to change to certificate for, click on the button next to the Server Certificate field and select Select from Certificate Store...
- Choose the new certificate from the certificate store.
- Confirm your selection and restart the MailStore Server service.
Importing an Existing Certificate
Typically certificates are exchanges between computers by means of Personal Information Exchange (PFX) containers. These can, for example, be created using the export functions of the MMC Snap-In Certificates.
Optional: Creating a PFX Container with OpenSSL/LibreSSL
When the original CSR was not created with Windows' own tools or not even created on a Windows computer, it is unlikely that the private key or the vertificate is available in Windows' certificate store of the MailStore Server computer, but on stored on the file system instead.
In this case, a Personal Information Exchange (PFX) container need to be created first. This needs to contain the certificate, private key, and all certificates of the certificate chain. After that, the PFX container can by imported into Windows' certificate store.
The following steps need to be executes to convert the certificate files into a PFX container with OpenSSL or LibreSSL:
- Copy the certificate, private key and the certificates of the certificate chain into the OpenSSL or LibreSSL directory.
- Open an elevated command prompt and navigate to this directory.
- Create the PFX container by executing the following command, adjust the file names of necessary:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out certificate.pfx -inkey privateKey.key -in certificate.crt -certfile CACert.crt
Importing a PFX container
- Open the MailStore Server Service Configuration.
- Select IP Addresses and Ports.
- In the section you want to change to certificate for, click on the button next to the Server Certificate field and select Import from file...
- Choose the PFX file.
- If the PFX file has been password protected, you are being ask to provide the password now.
- Confirm your selection and restart the MailStore Server service.