Archiving Emails from Microsoft Exchange 2007
Please note: This tutorial only covers the specifics of archiving a Microsoft Exchange 2007 server. It is assumed that you already have a MailStore Server installation or test installation and are familiar with the fundamentals of MailStore Server. Please refer to the Manual or the Quick Start Guide for more information.
MailStore Server offers several ways to archive emails from a Microsoft Exchange 2007 server, which are described below. If you are not sure which archiving method best suits your company, please refer to chapter Choosing the Right Archiving Strategy.
Synchronizing Users
As Microsoft Exchange requires the existence of an Active Directory, it is recommended to set up a synchronization as described in chapter Active Directory Integration of the MailStore Server manual.
Archiving Individual Mailboxes
Includes:Archiving an Exchange Mailbox
Archiving Multiple Exchange Mailboxes Centrally
With MailStore, some or all mailboxes of an Exchange server can be archived in a single step. All necessary preparations, such as creating MailStore users, can be made automatically. The archiving process can be executed manually or automatically according to a schedule.
Step 1: Setting up a central user for accessing mailboxes
Before the archiving process can be set up in MailStore, a user with access to all mailboxes to be archived has to be created. The corresponding method is called impersonation in Microsoft Exchange.
The following preconditions have to be met to be able to configure Exchange Impersonation:
- Administrative access to the Microsoft Exchange 2007 system on which the Client Access Role is installed
- Domain Administrator privileges
The following commands are executed in the Microsoft Exchange Management Shell:
Add access privileges
Get-ClientAccessServer ` | Add-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-Impersonation
Get-MailboxDatabase ` | Add-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-May-Impersonate
Important notice: [email protected] is the user account in UPN (User Principal Name) notation which you will use to access the mailboxes from MailStore. Please make sure that this user is not a member of any Exchange or Windows administrative group.
Check access privileges
Get-ClientAccessServer ` | Get-Adpermission -User [email protected] ` | Format-List *
Get-MailboxDatabase ` | Get-Adpermission -User [email protected] ` | Format-List *
Remove access privileges
Get-ClientAccessServer ` | Remove-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-Impersonation
Get-MailboxDatabase ` | Remove-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-May-Impersonate
Step 2: Configuration of MailStore Server
Includes:Centrally Archiving Multiple Exchange Mailboxes
Archiving Incoming and Outgoing Emails Directly
With the support of the Exchange Server Journaling functionality, MailStore can archive the incoming and outgoing emails of all users automatically. This is the only way to ensure that all emails are archived in their entirety.
Basic Functionality
Microsoft Exchange Server provides the option to take down all incoming, outgoing and internal email traffic. At the time of sending and receiving, a copy of the respective email is created and stored in a mailbox called Journal Mailbox. Additionally, the email is provided with a Journal report containing information about the actual senders and recipients.
MailStore can be configured to archive this Journal mailbox at regular intervals. During this process, the emails from the Journal mailbox will be assigned to their respective MailStore users (i.e. their user archives) automatically. This means that each user is able to view only their own emails.
Before the archiving process can be set up in MailStore, Journaling has to be set up for the Exchange server. Please proceed as follows:
Step 1: Creating a Mailbox for Journaling
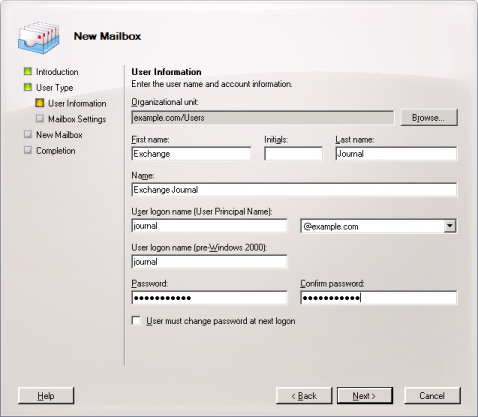
Set up a new Exchange user with a meaningful name, e.g. journal:
- Start the Exchange Management Console and click on Recipient Configuration.
- Click on New Mailbox.
- Select User Mailbox and click on Next.
- Select New User and click on Next.
- Enter journal as user name (see screen shot below) and click on Next.
- Click on Browse to select a mailbox database and click on Next.
- Confirm the summary by clicking on New. The user journal is created.
Step 2: Configuring Exchange Journaling
Two types of journaling are available in Exchange 2007: standard and premium journaling. While standard journaling always includes all send and received emails of a mailbox database, premium journaling can be limited to particular recipients or distribution lists and the scope (internal, external, global) of the journal rule can be defined. Additionally premium journaling rules can be replicated throughout the whole Exchange organization.
Notice: Premium journaling requires Exchange Enterprise CALs.
Configure Standard Journaling
Open the Exchange Management Console. In the tree structure, open Server Configuration and then Mailbox.
- Click on the Database Management tab.
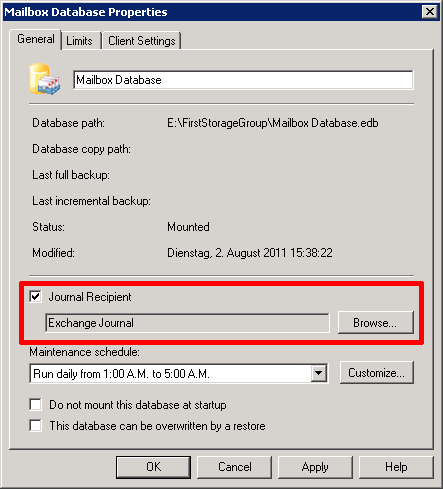
- Right click on the mailbox database for which you want to set up standard journaling and select Properties.
- Tick Journal Recipient and click on Browse
- Select the user from the recipient list that was created in step 1 and confirm with OK
- The following screenshot shows an example of a standard journaling configuration:
- To confirm the changes and active the journaling, click on OK.
Once the new configuration has come into effect, a copy of all incoming and outgoing emails is stored in the Journal mailbox (along with a report). MailStore can now be configured to archive the Journal mailbox in regular intervals as described below.
Configure Premium Journaling
Open the Exchange Management Console. In the tree structure, open Organization Configuration and then Hub Transport.
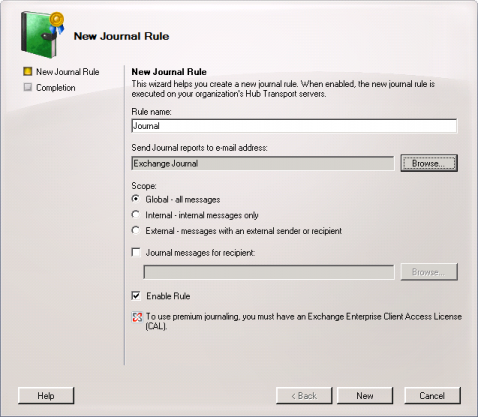
- Click on the Journaling tab and in the area on the right on New Journal Rule.
- The dialog window New Journal Rule opens:
- Enter a name for the Journal rule, e.g. journal.
- Click on Browse and select the user journal created above.
- Under Scope, choose Global to capture all messages, Internal to capture internally sent messages only, or External to capture only those messages with an external sender or recipient.
- Make sure that the checkbox Enable Rule is activated.
- Click on New to activate the rule. Please keep in mind that in complex Microsoft Exchange environments it may take several minutes until the new rule becomes effective.
Once the new configuration has come into effect, a copy of all incoming and outgoing emails is stored in the Journal mailbox (along with a report). MailStore can now be configured to archive the Journal mailbox in regular intervals as described below.
Step 3: Configuration of MailStore Server
Includes:Archiving an Exchange Journal Mailbox
Public Folders
MailStore Server can archive the emails from the public folders of Microsoft Exchange servers and make them available to some or all MailStore users. The archiving process can be executed manually or automatically according to a schedule.
Preparation
During archiving, emails are always assigned to individual users. Even when archiving a public folder, the user (or the user archive), for whom the emails are to be archived, has to be specified.
For this reason, first create a MailStore user for whom the public folder is to be archived. This user can be called publicfolder, for example. Next, all other users can be given access to the archive of the user publicfolder. This way, the archived content of the public folder is available to all MailStore users.
If MailStore users are not to have access to the archived public folder, skip this step and simply archive the emails to the user archive of the administrator (admin).
Information about how to create a new user in MailStore is available in the chapter User Management.
If you want to use Exchange Impersonation for a Service Account to archive public folders hosted on an Exchange 2007 Server, please execute the following command in the Microsoft Exchange Management Shell:
Add Permissions
Get-PublicFolderDatabase ` | Add-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-May-Impersonate
Check Permissions
Get-PublicFolderDatabase ` | Get-Adpermission -User [email protected] ` | Format-List *
Delete Permissions
Get-PublicfolderDatabase ` | Remove-AdPermission -User [email protected] -ExtendedRights ms-Exch-EPI-May-Impersonate
Includes:Archiving an Exchange Public Folder
Shared mailboxes are not primarily associated with individual users and are generally configured to allow logon access for multiple users.
Although it is possible to grant additional users the logon rights to any mailbox type, shared mailboxes are dedicated for this functionality. The Active Directory user associated with a shared mailbox must be a disabled account. After you create a shared mailbox, you must grant permissions to all users that require access to the shared mailbox.
As the active directory account of a shared mailbox is disabled, neither the Multiple Mailboxes nor the Single Mailbox archiving profiles can be used in MailStore.
In order to archive emails from a shared mailbox you must grant a user account full access to that mailbox (either by delegated access or impersonation). This can be the service account you created in Archiving Multiple Exchange Mailboxes Centrally.
Once you have created the service account, setup a new Single Mailbox archiving profile. Enter the credentials of the service account and fill the optional Mailbox field with the e-mail address of your shared mailbox.
Further steps are analogue to the archiving of individual Exchange mailboxes, except that you have to point the target archive to a separate dummy user in order to grant other MailStore users access to that archive.
Troubleshooting
The settings described above work in most cases. Yet, depending on the configuration of Microsoft Exchange Server, it is possible that a connection or registration fails even if all data has been entered correctly. If the suggestions in the corresponding error messages do not eliminate the problem, please try one or more of these alternative settings:
- Use HTTP instead of HTTPS.
- Make sure that the field Mailbox (opt.) contains the user's email address if it is different from the user's Windows login name.
- Use IMAP (unencrypted), IMAP-TLS or IMAP-SSL (both encrypted) instead of HTTP(S). To use IMAP, it has to be activated in Exchange.