Übersicht: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| [unmarkierte Version] | [unmarkierte Version] |
(Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „de:Übersicht en:Overview“) |
|||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| + | Dieser Artikel gibt einen allgemeinen Überblick über die grundlegenden Konzepte hinter MailStore Gateway. Es soll dazu dienen, besser zu verstehen, in welchen Einsatzszenarien MailStore Gateway im Zusammenspiel mit MailStore Server und MailStore Service Provider Edition verwendet werden kann. Detailliertere Ausführungen finden sich in den entsprechenden Artikeln dieser Hilfe, der MailStore Server Hilfe, oder der Hilfe der MailStore Service Provider Edition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | MailStore Gateway wurde vorrangig für zwei ausgewählte Szenarien konzipiert: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Um das Ziel einer Journal- oder Archivierungsregel auf anderen E-Mail-Servern zu dienen, welche selbständig Kopien von ein- und ausgehenden Nachrichten anfertigen könnenn. | ||
| + | # Um als SMTP- und POP3-Proxy zu dienen, welcher Kopien aller zwischen E-Mail-Clients und E-Mail-Server ausgetauschten E-Mails anfertigt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beide Einsatzszenarien werden in den folgenden Abschnitten detaillierter Vorgestellt. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MailStore Gateway als Server == | ||
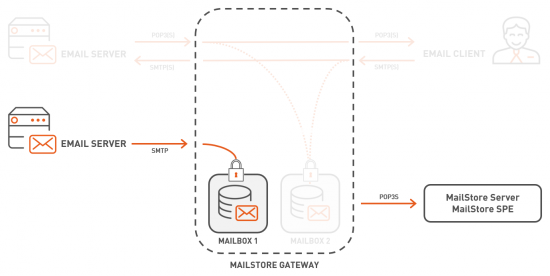
| + | Many email servers allow the creation of copies of all in- and outbound emails for the purpose of archiving. While on-premises email servers generally allow to deliver these copies into local mailboxes, most cloud based services (e.g. Microsoft Office 365, Google G Suite) do not, neither technically nor license-wise, and thus require external mailboxes to be used as a journal or archiving mailboxes. For those services, third-party archiving solutions, such as MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition, must either pull the emails from those external mailboxes, or, to circumvent that, be able to receive emails via SMTP directly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As direct SMTP archiving is generally preferred over using yet another third-party mailbox provider, MailStore Gateway provides this functionality for MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition without changing their basic concept of pull-only archiving. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This chart gives a good overview of the whole setup. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MailStore_Gateway_Overview_Server.png|550px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The typical workflow to set up this scenario looks as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # A MailStore Gateway [[Management Console#Create Mailbox|mailbox is created]]. Each MailStore Gateway mailbox has a unique email address. | ||
| + | # On the email server, a new journal or archiving rule is created. This rule uses the email address of a MailStore Gateway mailbox as target. | ||
| + | # Through the rule, copies of the emails to be archived are sent to MailStore Gateway via SMTP. Received emails are stored encrypted with an encryption key unique to each mailbox. | ||
| + | # MailStore Server or MailStore Service Provider Edition will then archive those emails from MailStore Gateway mailboxes via the corresponding archiving profile. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MailStore Gateway as Proxy == | ||
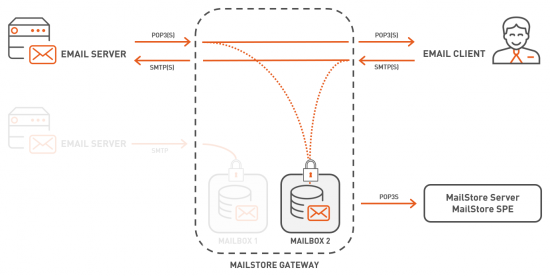
| + | Organizations without their own email server and without using an email service that allows to create journal or archiving rules as described before, may use the combination of POP3/SMTP on their email clients to receive and send emails. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To archive all in- and outbound emails in such a scenario, MailStore Gateway can record the communication between the email client and the email server, effectively operating as an email proxy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This chart gives a good overview of the whole setup. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MailStore_Gateway_Overview_Proxy.png|550px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The typical workflow to set up this scenario looks as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # A MailStore Gateway [[Management Console#Create Mailbox|mailboxes is created]]. Each MailStore Gateway mailbox has a unique identifier. | ||
| + | # On the email client, the in- (POP3) and outbound (SMTP) server must be replaced by the MailStore Gateway's IP address or host name. Additionally, the user name needs to be modified to '''remote_username%target_server%mailbox_id''' where | ||
| + | #* ''remote_username'' is the user name (e.g. [email protected]) to login to a mailbox on ''target_server'' | ||
| + | #* ''target_server'' is the IP address or host name of the original email server (e.g. mail.example.com) | ||
| + | #* ''mailbox_id'' is the unique identifier of the MailStore Gateway mailbox into which copies of the sent or received emails are to be stored. | ||
| + | # Once such changes have been made, copies of all send and received emails on that particular client are stored in the given MailStore Gateway mailbox. MailStore Gateway encrypts all stored emails with a key unique to the mailbox. | ||
| + | # Repeat step 2 in all email clients where the user's emails should be archived. | ||
| + | # In the last step, MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition will archive the messages from MailStore Gateway mailboxes via the corresponding email archiving profile. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Sicherheit == | ||
| + | Alle E-Mails, welche in MailStore Gateway Postfächern abgelegt werden, sind durch starke, hybride Verschlüsselung geschützt. Das Kennwort des Postfachs repräsentiert die Passphrase des privaten Schlüssels des asymmetrischen Teils der hybriden Verschlüsselung. Dies bedeutet, dass ohne das korrekte Postfach-Kennwort keine Daten entschlüsselt werden können. Daher wird dringend empfohlen, ein Postfach-Kennwort an einem sicheren Ort aufzubewahren (z.B. in einem Enterprise Password Manager). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Zusätzlich erlaubt es MailStore Gateway nicht, Benutzernamen oder Kennwörter über eine unverschlüsselte Verbindung zu übertragen. Dies macht es erforderlich, dass entfernte Server, zu welchen über die Proxy-Funktionalität eine Verbindung aufgebaut wird, implizite (SMTPS, POP3S) oder explizite (SMTP+STARTTLS, POP3+STARTTLS) Verschlüsselung unterstützt wird. | ||
| + | |||
[[de:Übersicht]] | [[de:Übersicht]] | ||
[[en:Overview]] | [[en:Overview]] | ||
Version vom 5. März 2019, 15:28 Uhr
Dieser Artikel gibt einen allgemeinen Überblick über die grundlegenden Konzepte hinter MailStore Gateway. Es soll dazu dienen, besser zu verstehen, in welchen Einsatzszenarien MailStore Gateway im Zusammenspiel mit MailStore Server und MailStore Service Provider Edition verwendet werden kann. Detailliertere Ausführungen finden sich in den entsprechenden Artikeln dieser Hilfe, der MailStore Server Hilfe, oder der Hilfe der MailStore Service Provider Edition.
MailStore Gateway wurde vorrangig für zwei ausgewählte Szenarien konzipiert:
- Um das Ziel einer Journal- oder Archivierungsregel auf anderen E-Mail-Servern zu dienen, welche selbständig Kopien von ein- und ausgehenden Nachrichten anfertigen könnenn.
- Um als SMTP- und POP3-Proxy zu dienen, welcher Kopien aller zwischen E-Mail-Clients und E-Mail-Server ausgetauschten E-Mails anfertigt.
Beide Einsatzszenarien werden in den folgenden Abschnitten detaillierter Vorgestellt.
MailStore Gateway als Server
Many email servers allow the creation of copies of all in- and outbound emails for the purpose of archiving. While on-premises email servers generally allow to deliver these copies into local mailboxes, most cloud based services (e.g. Microsoft Office 365, Google G Suite) do not, neither technically nor license-wise, and thus require external mailboxes to be used as a journal or archiving mailboxes. For those services, third-party archiving solutions, such as MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition, must either pull the emails from those external mailboxes, or, to circumvent that, be able to receive emails via SMTP directly.
As direct SMTP archiving is generally preferred over using yet another third-party mailbox provider, MailStore Gateway provides this functionality for MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition without changing their basic concept of pull-only archiving.
This chart gives a good overview of the whole setup.
The typical workflow to set up this scenario looks as follows:
- A MailStore Gateway mailbox is created. Each MailStore Gateway mailbox has a unique email address.
- On the email server, a new journal or archiving rule is created. This rule uses the email address of a MailStore Gateway mailbox as target.
- Through the rule, copies of the emails to be archived are sent to MailStore Gateway via SMTP. Received emails are stored encrypted with an encryption key unique to each mailbox.
- MailStore Server or MailStore Service Provider Edition will then archive those emails from MailStore Gateway mailboxes via the corresponding archiving profile.
MailStore Gateway as Proxy
Organizations without their own email server and without using an email service that allows to create journal or archiving rules as described before, may use the combination of POP3/SMTP on their email clients to receive and send emails.
To archive all in- and outbound emails in such a scenario, MailStore Gateway can record the communication between the email client and the email server, effectively operating as an email proxy.
This chart gives a good overview of the whole setup.
The typical workflow to set up this scenario looks as follows:
- A MailStore Gateway mailboxes is created. Each MailStore Gateway mailbox has a unique identifier.
- On the email client, the in- (POP3) and outbound (SMTP) server must be replaced by the MailStore Gateway's IP address or host name. Additionally, the user name needs to be modified to remote_username%target_server%mailbox_id where
- remote_username is the user name (e.g. [email protected]) to login to a mailbox on target_server
- target_server is the IP address or host name of the original email server (e.g. mail.example.com)
- mailbox_id is the unique identifier of the MailStore Gateway mailbox into which copies of the sent or received emails are to be stored.
- Once such changes have been made, copies of all send and received emails on that particular client are stored in the given MailStore Gateway mailbox. MailStore Gateway encrypts all stored emails with a key unique to the mailbox.
- Repeat step 2 in all email clients where the user's emails should be archived.
- In the last step, MailStore Server and MailStore Service Provider Edition will archive the messages from MailStore Gateway mailboxes via the corresponding email archiving profile.
Sicherheit
Alle E-Mails, welche in MailStore Gateway Postfächern abgelegt werden, sind durch starke, hybride Verschlüsselung geschützt. Das Kennwort des Postfachs repräsentiert die Passphrase des privaten Schlüssels des asymmetrischen Teils der hybriden Verschlüsselung. Dies bedeutet, dass ohne das korrekte Postfach-Kennwort keine Daten entschlüsselt werden können. Daher wird dringend empfohlen, ein Postfach-Kennwort an einem sicheren Ort aufzubewahren (z.B. in einem Enterprise Password Manager).
Zusätzlich erlaubt es MailStore Gateway nicht, Benutzernamen oder Kennwörter über eine unverschlüsselte Verbindung zu übertragen. Dies macht es erforderlich, dass entfernte Server, zu welchen über die Proxy-Funktionalität eine Verbindung aufgebaut wird, implizite (SMTPS, POP3S) oder explizite (SMTP+STARTTLS, POP3+STARTTLS) Verschlüsselung unterstützt wird.