Archiving Server Mailboxes
This chapter describes how a single mailbox located on any email server can be archived using the IMAP or POP3 protocols. To archive multiple mailboxes in one step, Batch-archiving IMAP Mailboxes can be used. If the mailbox is a multidrop mailboxes, also called catchall mailboxes, that contains emails for more than one person please read the chapter Archiving IMAP and POP3 Multidrop Mailboxes
Important: This article describes the general procedure independent from the e-mail server used. Please find e-mail server specific information in our Implementation Guides.
Required Information
In order to archive a server mailbox, MailStore requires the following data:
- The server name (e.g. imap.myserver.com).
- The protocol used (e.g. IMAP-TLS).
- The user name. Often times, the full email address or the local part (left of the @ character) is used.
- The password.
IMAP or POP3?
When choosing between IMAP and POP3, we strongly recommend using IMAP. With IMAP, all or specific folders of the mailbox can be archived. POP3 does not "recognize" any folders; because of this it is likely that, with most service providers, only the inbox will be archived.
Setting Up the Archiving Process
By following the procedure described here, a single mailbox can be archived for a specific MailStore user. The archiving process can be executed manually or automatically.
Setting up archiving processes for IMAP or POP3 mailboxes is done using archiving profiles. General information about archiving profiles is available in chapter Working with Archiving Profiles.
For each mailbox, please proceed as follows:
- Users can only archive their own mailboxes to their personal user archive. To archive the emails of other users, you have to be logged on to MailStore Client as MailStore administrator. Only MailStore administrators can archive the emails of other users.
- In MailStore, click on Archive Email.
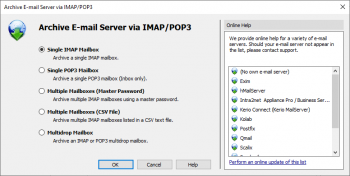
- To create a new archiving profile, select Other Server via IMAP/POP3 from the Email Servers list in the Create Profile area of the application window.
- A wizard opens guiding you through the setup process.
- Select Single Mailbox and click on OK.
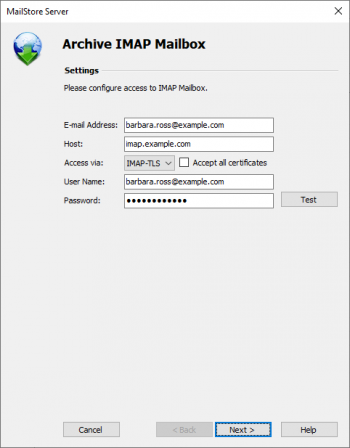
- Fill out the fields Email Address, Host, Access via, User Name and Password. The Email Address is used to label the folder that is created in the archive by this profile. Click on Test to verify the data entered.
- For the IMAP-TLS and IMAP-SSL protocols only: If the certificate provided by the remote host cannot be verified (e.g. self-signed or signed by an unknown certificate authority), enable the option Accept all certificates to allow MailStore to establish a connection. As this option leads to an insecure configuration, warnings may appear in the summary and/or the dashboard.
- Click on Next.
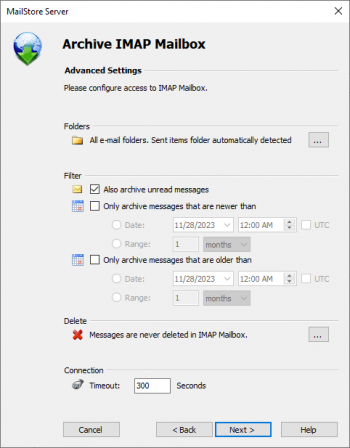
- Customize the list of folders to be archived (IMAP only), the filter (IMAP only) and the deletion rules. By default, no emails will be deleted from a mailbox. The timeout value only has to be adjusted as needed (e.g. with very slow servers).
- Click on Next.
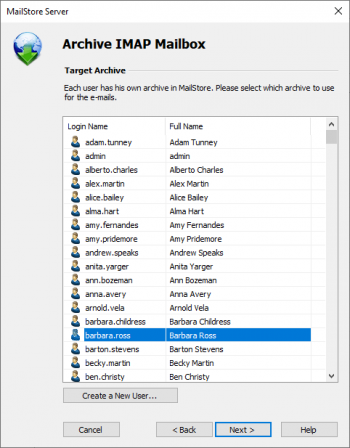
- If logged on to MailStore Server as administrator, the target archive can be specified at the next step. Select the archive of the user for whom the mailbox is to be archived.
- At the last step, a name for the new archiving profile can be specified. After clicking on Finish, the archiving profile will be listed under Saved Profiles and can be run immediately, if desired.
Starting the Archiving Process
Starting the Archiving Process Manually
On the start page of MailStore Client, click on Archive Email and from the list under Saved Profiles, select the appropriate archiving profile. Click on Run. After the archiving process has been executed, a protocol appears. It contains information about the volume of emails that have been archived as well as any errors that may have occurred.
This process can be repeated by the user any number of times. MailStore only archives those emails that are not yet stored in the corresponding user archive.
Automating the Archiving Process
In addition to being executed manually, archiving tasks can also be executed automatically. Additional information about this topic is available in chapter Automating the Archiving Process.